
Language of Vectors (LangVec) is a simple Python library designed for transforming numerical vector data into a language-like structure using a predefined set of words (lexicon).
Approach
LangVec package leverages the concept of percentile-based mapping to assign words from a lexicon to numerical values,
facilitating intuitive and human-readable representations of numerical data.
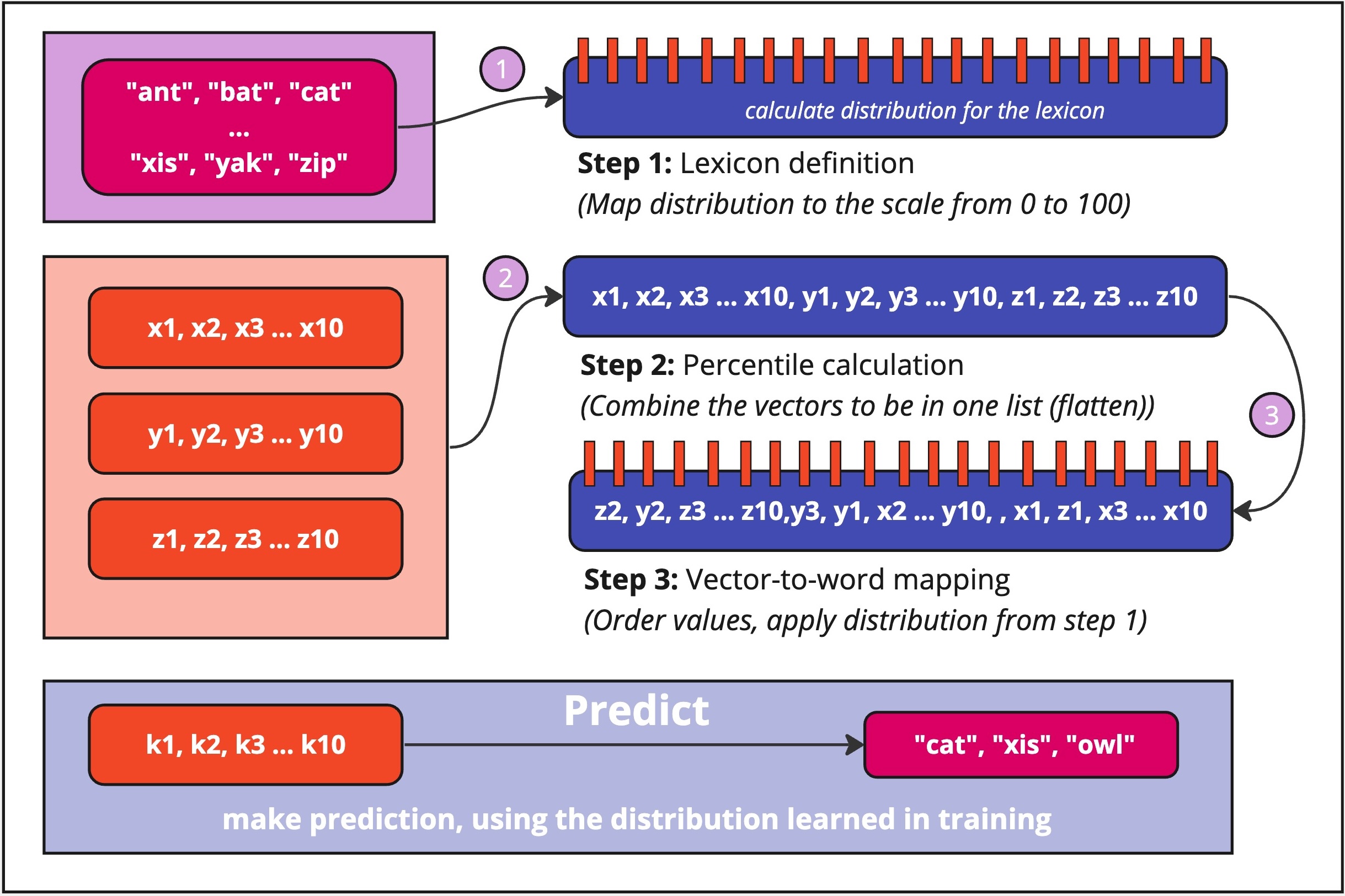 Simplified schema of how LangVec works
Simplified schema of how LangVec works
Where to use LangVec
The main application is in semantic search and similarity-based systems, where understanding the proximity between
vectors is crucial.
By transforming complex numerical vectors into a lexicon-based representation, LangVec facilitates an intuitive
understanding of these similarities for humans.
In fields like machine learning and natural language processing, LangVec can assist in tasks such as clustering or
categorizing data, where a human-readable format is preferable for quick insights and decision-making.
Installation
pip install langvec
Usage
Example 1
import numpy as np
from langvec import LangVec
# Random seed
np.random.seed(42)
# Initialize LangVec
lv = LangVec()
NUM_VECTORS = 1000
DIMENSIONS = 10
# Generate some random data
vectors = [np.random.uniform(0, 1, DIMENSIONS) for _ in range(NUM_VECTORS)]
# Fit to this data (getting know to distribution)
lv.fit(vectors)
# Save current model
lv.save("model.lv")
# Example vector for prediction
input_vector = np.random.uniform(0, 1, DIMENSIONS)
# Make prediction on unseen vector embedding
print(lv.predict(input_vector))
Example 2
import string
import numpy as np
from langvec import LangVec
np.random.seed(42)
# Define a new lexicon with lowercase and uppercase letters
LEXICON = list(string.ascii_letters)
# Initialize LangVec with the new lexicon
lv = LangVec(lexicon=LEXICON)
NUM_VECTORS = 10000
DIMENSIONS = 256
# Generate some random data
vectors = [np.random.uniform(0, 1, DIMENSIONS) for _ in range(NUM_VECTORS)]
# Fit to this data
lv.fit(vectors)
# Example vector for prediction
input_vector = np.random.uniform(0, 1, DIMENSIONS)
# Make prediction on the unseen vector embedding
predicted_string = "".join(lv.predict(input_vector))
print(predicted_string)
if len(predicted_string) > 6:
summarized_string = (
"".join(predicted_string[:3]) + "..." + "".join(predicted_string[-3:])
)
else:
summarized_string = "".join(predicted_string)
print(summarized_string)
Save and load model from disk
LangVec allows you to save and load percentiles as model artifacts. This is useful for preserving the learned distribution without needing to retrain the model. You can use the following methods:
Save model
from langvec import LangVec
# Initialize LangVec
lv = LangVec()
# Save the model to file
lv.save("model.lv")
Load model
from langvec import LangVec
# Initialize LangVec
lv = LangVec()
# Load the model from file
lv.load("model.lv")
Citation
If you use LangVec in your research, please cite the following paper:
Emanuilov, S. and Dimov, A., 2024. Lexical representation of dense numerical vectors: Introducing LangVec. Mathematics & Informatics, 67(3).